28 Mar ProFlora Blend & GI Renew
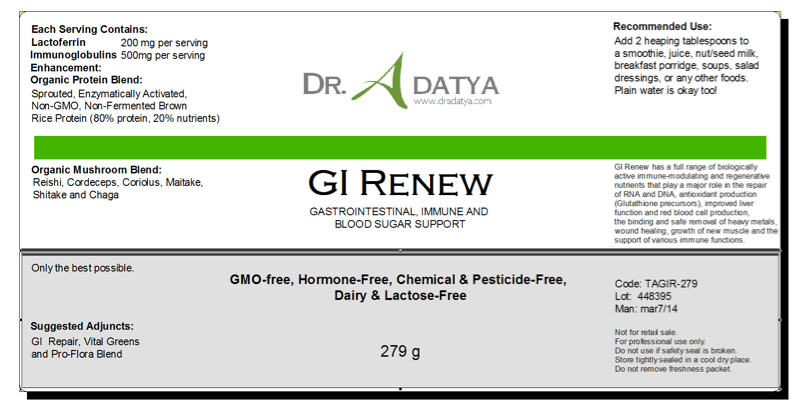
GI Renew
All of Dr. Adatya’s formulations are only available at the Pure Pharmacy on 3750 Oak St (Oak & W. 22nd). Pure also ships & delivers, call them at: 604-731-8535. PST-free.
No Fillers! Stevia-Free, Gluten-free, Dairy-free, Lactose-Free, Soy-Free, GMO-free. Organic and Wild-Crafted where applicable. Hypoallergenic and medicinal grade.
GI Renew is an immune-strengthening, anti-inflammatory formula combining high levels of lactoferrin, immunoglobulins, glutathione precursors and growth factors along with a 6 species blend of organic, hot water extracted medicinal mushrooms (Reishi, Coriolus, Siitake, Maitake, Chaga, Cordyceps). The structures found in these medicinal mushrooms includes Beta 1-3 Glucan, Beta 1-6, 1-3 Glucan, Beta 1-4, 1-3, 1-6 Glucan and Beta 1-6 Glucan.
With the added sprouted, non-fermented hypoallergenic brown rice protein, this formula also supports healthy blood sugar balance.
Quite simply stated, GI Renew is radically different in terms of its constituent profile and effective levels of the immunologically important active compounds that define this supplement as “medicinal” offering full spectrum immune support.
While you might hear the word bacteria and associate it with something negative, there are many beneficial bacteria that our digestive system needs to stay healthy. The bacterial composition of your gut is very important to not only your digestion, but also to your health in general. Maintaining a proper balance of bacteria in your gastrointestinal system means increasing the beneficial, “good” bacteria while decreasing the harmful, “bad” bacteria. Probiotics help keep this balance.
Probiotics
These are live bacteria that have a beneficial effect on the body when ingested. When these bacteria get to the digestive system, they colonize and flourish, limiting the concentration of harmful bacteria. They may also influence enzyme activity to help aid digestion. Probiotics can be ingested either through a supplement or through foods with live cultures such as fermented foods.
Probiotics have many benefits:
- They improve digestion and fight diarrhea.
- They enhance immune function.
- They benefit lipid metabolism.
- They have antioxidant properties and exhibit anti-cancer effects.
- They have wide ranging effects that can benefit lung, skin, and joint health
How to pick your probiotics
Many food manufacturers are jumping on the benevolent bacteria bandwagon, but a large proportion of grocery store products simply do not deliver the benefits of probiotics because they lack the potency and nutrition of a true supplement. A single dose of probiotic supplement should have a MINIMUM of 10 million live bacteria, an ideal amount would be 20 million. It is also clear that these bacteria should be from MORE than one of the Lactobacillus family, in fact they should include the most common non-competing human flora strains – which are just about the only ‘friendly-bacteria’ tough enough to make it into the large intestine where they need to be. After a course of antibiotics, I suggest patients take between 20 and 40 BILLION everyday for a week just to re-inoculate, followed by 20 billion daily just to keep bowels in top form. You can experiment with different amounts to see what works best for you, but if you are only just beginning to take probiotics, I would start with a rather high dose.
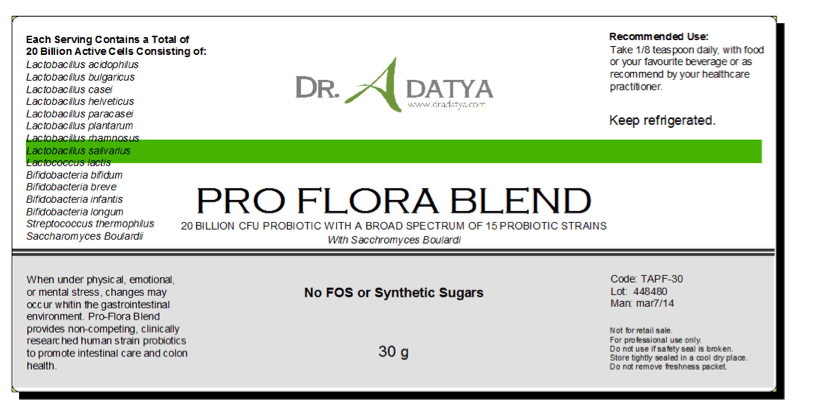
ProFlora Blend
I formulated this probiotic blend from evidence-based research pulled from peer-reviewed journals. A single serving delivers 20 billion of the 14 human flora strains– the whole species of acidophilus, lactobacillus, bifidus, rhamnosus, plus saccharomyces boulardi. The ProFlora blend contains no FOS, a common synthetic sugar found in many probiotics. It must be refrigerated and taken with food.
References
J Ren Nutr. 2002 Apr;12(2):76-86.
J Appl Microbiol. 2006 Jun;100(6):1171-85.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb;27(1):139-55.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2014;54(7):938-56.
J Med Food. 2013 Mar;16(3):223-9.
Food Chem. 2012 Dec 1;135(3):1914-9.
Food Microbiol. 2011 Aug;28(5):1062-71.
The J of Alt and Comp Med. 1998(4):289-303
Hobbs, C., Medicinal Mushrooms, Botanica Press. 1995
Abstracts of Chinese Medicine, 1:371. 1985.

